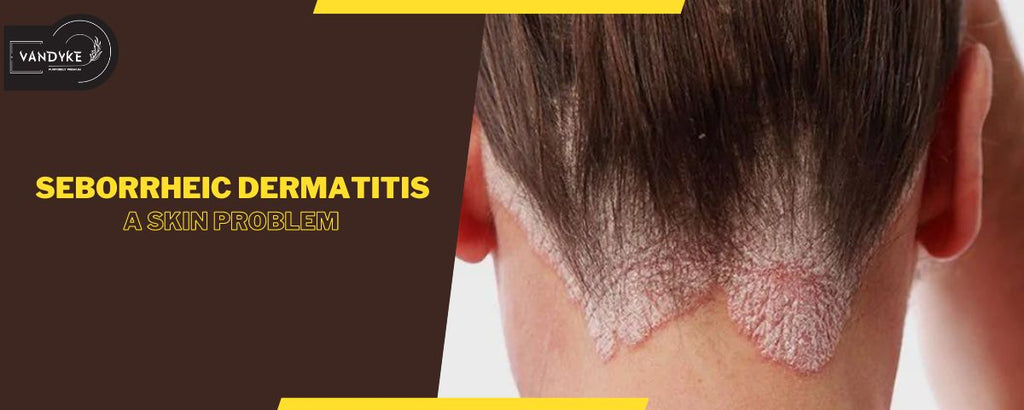
Is Seborrheic Dermatitis A skin Problem?

Seborrheic Dermatitis: A skin Problem
Definition of seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterised by red, inflamed patches, and flaky scales. It commonly affects areas rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. The condition involves an overgrowth of yeast, contributing to skin irritation and often resulting in persistent itching and discomfort.
Common Areas Affected
Seborrheic dermatitis commonly affects regions with a high density of sebaceous (oil) glands. The scalp is a frequent target, leading to dandruff and sometimes causing red, itchy patches. The face, particularly around the eyebrows, nose, and ears, may exhibit symptoms such as redness and flaky skin. Additionally, seborrheic dermatitis can extend to the chest, back, and other body areas with increased sebum production, presenting as irritated patches with scaling. These manifestations often occur in regions where skin folds, such as the armpits and groyne, creating discomfort. Understanding the typical areas affected is crucial for recognizing and addressing the condition, as different regions may require specific care and treatment approaches.
Chronic and Recurring Nature
Seborrheic dermatitis stands out for its chronic and recurrent nature, often becoming a persistent aspect of an individual’s life. Unlike some skin conditions that may resolve with time, seborrheic dermatitis tends to linger over the long term. Even when symptoms temporarily improve, they commonly recur, necessitating ongoing management. The chronicity of seborrheic dermatitis underscores the importance of adopting consistent skincare routines and lifestyle adjustments to mitigate flare-ups. Individuals facing this condition should be prepared for a proactive approach to maintain skin health continuously. Seeking professional guidance to develop a personalised, sustainable management plan is crucial for effectively addressing the chronic and recurring nature of seborrheic dermatitis and enhancing the overall quality of life for those affected.
Causes
1.Factors contributing
Several factors contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Genetics plays a significant role, as individuals with a family history of the condition are more prone to experiencing it. An overgrowth of yeast, particularly Malassezia, on the skin contributes to inflammation and exacerbates symptoms. Hormonal changes, stress, and certain medical conditions can also trigger seborrheic dermatitis episodes. The condition is closely linked to excessive sebum production, creating an environment conducive to its manifestation. Recognizing these contributing factors is crucial for understanding the complexity of seborrheic dermatitis and tailoring effective treatment strategies to address its multifaceted origins.
2.Role of Sebum in Production in Skin Health
Sebum production plays a vital role in maintaining skin health, but an imbalance can contribute to conditions like seborrheic dermatitis. Sebum, an oily substance produced by the skin’s sebaceous glands, serves to moisturise and protect the skin. However, when there’s an overproduction or abnormal composition of sebum, it can create an environment conducive to the growth of Malassezia yeast, a key factor in seborrheic dermatitis. This overgrowth triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the characteristic redness, itching, and flaking associated with the condition. Striking a balance in sebum production through proper skincare practices is essential for preventing and managing seborrheic dermatitis, underscoring the intricate relationship between sebum and overall skin health.
Environmental factors and stress triggers
Environmental factors and stress are recognized triggers for seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups. Harsh weather conditions, such as cold and dry climates, can exacerbate symptoms by drying out the skin and disrupting its natural barrier. Environmental pollutants and allergens may also contribute to skin irritation. Moreover, stress, whether emotional or physical, plays a significant role in triggering or worsening seborrheic dermatitis episodes. Stress impacts the immune system and hormonal balance, potentially leading to increased inflammation. Understanding and managing these environmental factors and stressors are crucial components of an effective strategy to minimise the frequency and intensity of seborrheic dermatitis symptoms.
Symptoms
–Seborrheic dermatitis include red or inflamed skin, accompanied by persistent itching.
–The affected areas often develop flaky scales or crusts, contributing to the characteristic appearance of dandruff on the scalp.
–On the face, symptoms may manifest as patches of redness and flaky skin, particularly around the eyebrows, nose, and ears.
–Other common areas of involvement include the chest, back, and skin folds, where irritated patches with scaling can occur.
–The severity of symptoms can vary, with some individuals experiencing mild discomfort and others facing more pronounced inflammation and itching.
Recognizing these common symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective management of seborrheic dermatitis.
Potential Impact on Quality of Life
Seborrheic dermatitis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life due to its visible and often chronic nature. The persistent redness, flaking, and itching can be not only physically uncomfortable but also emotionally distressing. The visibility of symptoms, especially on the face and scalp, may lead to self-consciousness and a decreased sense of well-being. Individuals with seborrheic dermatitis might experience social and professional challenges, affecting their confidence and overall mental health. Additionally, the chronic and recurrent nature of the condition necessitates ongoing attention, potentially disrupting daily routines. Addressing both the physical symptoms and the emotional toll is crucial for enhancing the overall quality of life for those managing seborrheic dermatitis.
Diagnosis
How Dermatologists Diagnose Seborrheic Dermatitis
Dermatologists diagnose seborrheic dermatitis through a combination of visual examination and consideration of the patient’s medical history. The distinctive appearance of red, inflamed skin with flaky scales or crusts in common areas such as the scalp, face, and chest often aids in diagnosis. Dermatologists may inquire about symptoms, their duration, and potential triggers. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be conducted to rule out other conditions. While there isn’t a specific test for seborrheic dermatitis, dermatologists use their expertise to differentiate it from similar skin conditions. Seeking professional evaluation is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and the formulation of an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s specific needs.
Differential Diagnoses to Consider
When diagnosing seborrheic dermatitis, dermatologists must consider several differential diagnoses to rule out other skin conditions with similar symptoms. These may include:
- Psoriasis: Characterised by thick, red patches of skin with silvery scales.
- Contact Dermatitis: Inflammation resulting from skin contact with irritants or allergens.
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Chronic skin inflammation often associated with itching and dryness.
- Tinea (Ringworm): Fungal infections that can resemble seborrheic dermatitis but have different treatments.
- Rosacea: Chronic skin condition causing redness and visible blood vessels, primarily on the face.
- Allergic or Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Skin reactions due to contact with specific substances.
Considering these potential differential diagnoses is crucial for accurate identification and effective management of seborrheic dermatitis. Dermatologists rely on their expertise to distinguish between these conditions based on clinical presentation, history, and sometimes additional diagnostic tests.
Treatment Options
shampoos and creams
Using shampoo like our vandykes helps in reducing flakyness and dandruff from hair and to the some point redness and itchiness in the scalp and make hair stronger, smooth and silky. best in hair fall solution
Prescription medications
Prescription medications play a crucial role in treating seborrheic dermatitis, particularly in cases where over-the-counter products may not provide sufficient relief. Dermatologists may recommend the following prescription medications:
- Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications help alleviate redness, itching, and swelling. They are available in various strengths, and a dermatologist will prescribe the most suitable one based on the severity of symptoms.
- Topical Antifungals: Prescription-strength antifungal creams or ointments, such as ketoconazole or cicloprox, can target the overgrowth of yeast that contributes to seborrheic dermatitis.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are immunomodulators that can be prescribed for areas like the face and neck to control inflammation without using steroids.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: In severe cases, oral antifungal medications like fluconazole or itraconazole may be prescribed to address systemic fungal overgrowth.
- Topical Immunomodulators: These medications, such as pimecrolimus and tacrolimus, help modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation.
Natural remedies
While natural remedies may not replace prescribed medications, some individuals find relief from seborrheic dermatitis symptoms through these approaches. It’s important to note that results can vary, and consulting with a dermatologist is advisable. Here are some natural remedies that people may consider:
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, tea tree oil can be diluted and applied topically to affected areas.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera’s anti-inflammatory and soothing properties may help alleviate redness and irritation. Apply pure aloe vera gel to affected areas.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil’s moisturising properties can assist in reducing dryness. Apply a small amount to affected areas.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar may help regulate the skin’s pH. Use it as a rinse or in a compress, but avoid applying to open sores.
- Honey: With its antimicrobial properties, honey can be applied to affected areas. Ensure it’s pure and free from additives.
- Oatmeal Baths: Oatmeal’s anti-inflammatory properties can soothe irritated skin. Add colloidal oatmeal to warm bathwater.
Management and Prevention
Chronic Nature and Need for Long-Term Management
Seborrheic dermatitis demands a recognition of its chronic nature, requiring a commitment to long-term management strategies. Unlike transient skin issues, this condition often persists over time, necessitating consistent care for effective control. Individuals coping with seborrheic dermatitis should embrace a proactive approach, incorporating regular use of prescribed medications or medicated shampoos. Long-term management involves not only treating active symptoms but also adopting a preventive mindset to minimise the likelihood of flare-ups. Understanding that seborrheic dermatitis is an ongoing concern emphasises the importance of integrating dermatologist-recommended routines into daily life, fostering skin health and mitigating the recurrent nature of the condition. Seeking professional guidance ensures a tailored, sustainable approach to address the chronic aspects of seborrheic dermatitis and enhance the overall quality of skin care.
Importance of Consistent Skincare Routines
Consistency in a skincare routine is paramount for effectively managing seborrheic dermatitis. Establishing a regular regimen helps maintain skin health and minimise the impact of this chronic condition. Dermatologists often recommend gentle cleansers and medicated products tailored to seborrheic dermatitis. Adhering to a daily routine, including cleansing and application of prescribed treatments, creates a protective barrier against flare-ups. Consistency not only aids in controlling current symptoms but also plays a crucial role in preventing future episodes. Individuals should prioritise ongoing skincare habits, even during symptom-free periods, to address the persistent and recurrent nature of seborrheic dermatitis. A steadfast commitment to a personalised…
Preventive Measures to Reduce Flare-ups
Preventive measures are essential for minimising flare-ups in seborrheic dermatitis. Consider incorporating these strategies into your routine:
- Regular Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil and prevent the buildup of scales. Be mindful of not overwashing, as this can exacerbate dryness.
- Medicated Shampoos: Use medicated shampoos as recommended by your dermatologist to control yeast overgrowth on the scalp. Regular use, even during symptom-free periods, can prevent flare-ups.
- Moisturise: Apply a hypoallergenic moisturiser to keep the skin hydrated, reducing the likelihood of dryness and irritation.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and minimise exposure to triggers such as stress, harsh weather conditions, and certain skincare or hair products that may worsen symptoms.
- Sun Protection: Protect your skin from excessive sun exposure, as sunburn can trigger seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Practise stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to mitigate the impact of stress on your skin.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a well-balanced diet, stay hydrated, and get adequate sleep, as overall health can influence skin conditions.
- Regular Follow-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your dermatologist to monitor your skin’s health, adjust treatment plans, and address any emerging concerns promptly.
By integrating these preventive measures into your daily life, you can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups, promoting long-term skin wellness.
Conclusion:
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic skin condition characterised by red, inflamed patches, and flaky scales.Seborrheic dermatitis commonly affects regions with a high density of sebaceous (oil) glands.Seborrheic dermatitis stands out for its chronic and recurrent nature, often becoming a persistent aspect of an individual’s life.
Dermatologists diagnose seborrheic dermatitis through a combination of visual examination and consideration of the patient’s medical history. The distinctive appearance of red, inflamed skin with flaky scales or crusts in common areas such as the scalp, face, and chest often aids in diagnosis